What is Theobroma Cacao ?
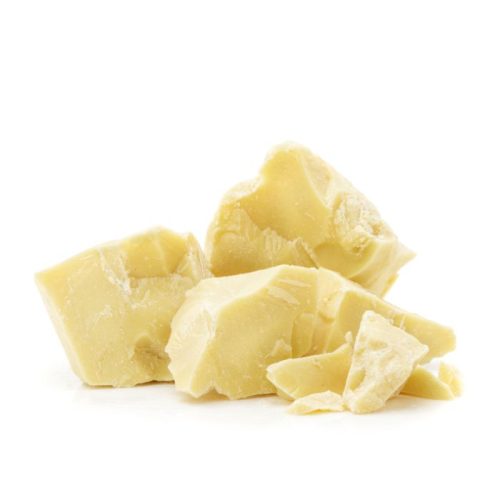
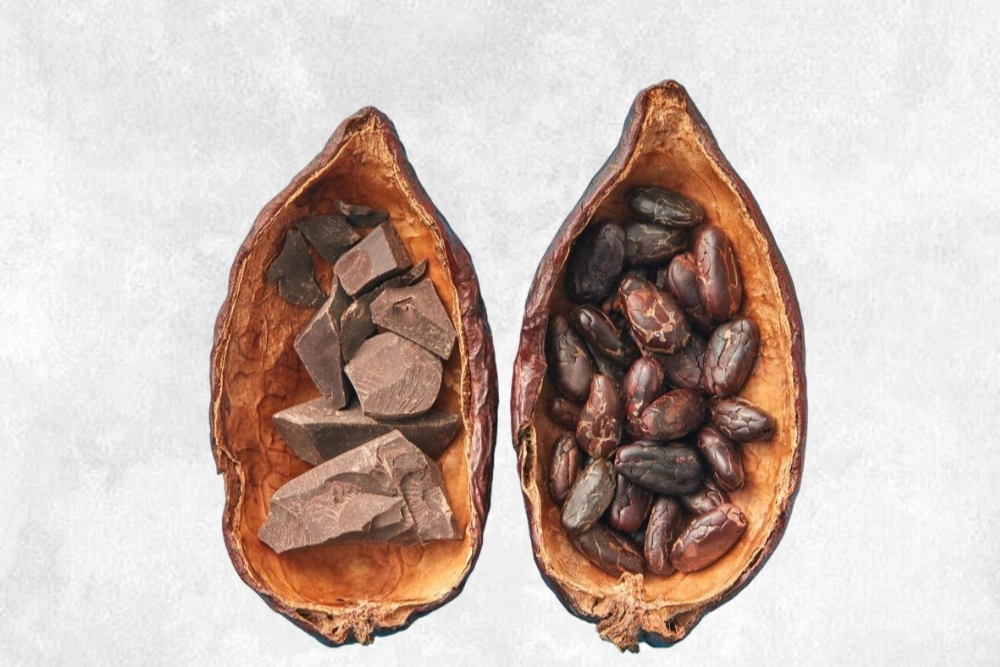
Theobroma Cacao is a tropical tree native to the rainforests of Central and South America. Its seeds, commonly known as cocoa beans, are not only the primary ingredient in chocolate production but also the source of cocoa butter, a natural plant-based fat extracted through pressing.
Cocoa beans are rich in:
Polyphenols: Powerful antioxidants that contribute to health benefits
Methylxanthines: Such as theobromine and caffeine, known for their stimulating effects
Essential minerals: Including magnesium and potassium
These components enhance the nutritional and therapeutic value of cocoa beans, making them valuable in both food and health industries.

Why Does Cocoa Butter Melt at Body Temperature? Melting Point and Crystal Structure
Cocoa butter melts easily at human body temperature (~37°C) due to its unique crystalline structure and balanced composition of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Its melting point typically ranges between 34°C and 38°C, perfectly aligning with body heat.
This behavior is attributed to polymorphism, the ability of cocoa butter to form multiple crystal structures. Out of six known crystalline forms, the Beta V (β5) form offers the ideal stability and melting point. This form allows chocolate to remain solid at room temperature while smoothly melting in the mouth.
Such characteristics are crucial when selecting cocoa butter for high-quality chocolate production, fast-absorbing cosmetics, and topical pharmaceuticals, where controlled melting and texture are essential.

Which Fatty Acids Are in Cocoa Butter and What Are Their Functions ?
Cocoa butter is a blend of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, each contributing to its chemical structure and functional properties. The three main fatty acids include:
Stearic Acid (C18:0):
A saturated fatty acid that enhances the firmness, structural integrity, and physical stability of cocoa butter. In chocolate manufacturing, it helps produce heat-resistant chocolates that retain shape at ambient temperatures.Palmitic Acid (C16:0):
Another saturated fatty acid crucial for extending product shelf life and providing resistance against oxidation. In cosmetics, these properties contribute to longer-lasting creams and lotions.Oleic Acid (C18:1):
An unsaturated fatty acid responsible for the softness, smoothness, and fluidity of cocoa butter. Essential for creating chocolates with a silky mouthfeel and fast melting. In skincare products, it improves hydration and enhances skin absorption.

What Is Cocoa Butter Made Of ? Composition and Chemical Structure Analysis
Cocoa butter is primarily composed of three major fatty acids: stearic acid, palmitic acid, and oleic acid. This unique composition gives cocoa butter its solid texture, a melting point close to body temperature, and oxidative stability. The chemical structure is the key factor behind its smoothness, rich flavor, and quick melt-in-mouth sensation.

Master the βV form ; read the guide that helps you achieve stable, glossy, bloom-resistant chocolate.
Beta5 Form : The Foundation of Stable , Shiny Chocolate
- Related Articles

How Do Cocoa Bean Origin and Type Affect Chocolate’s Color, Flavor and Crystal Structure?
The geographical origin of cocoa beans directly influences the fatty acid composition, color, flavor profile, and crystalline structure of chocolate:
African Cocoa Beans:
High in stearic acid, resulting in firmer texture, slower melting, and more stable crystalline structures. Chocolates made from African beans typically have a darker color and a stronger, more robust flavor.South American Cocoa Beans:
Richer in oleic acid, leading to a softer texture, lower melting point, and smoother mouthfeel. These chocolates often exhibit more fruity and complex flavor notes.Asian Cocoa Beans:
Offer a balanced composition of stearic and oleic acids, producing chocolate with a mid-range firmness, balanced texture, and moderate color intensity.
Choosing the right bean origin determines not only the physical properties and melting behavior of chocolate but also its flavor profile and aroma. This selection is critical for sourcing raw materials in premium chocolates, specialty products, and even cosmetic applications.
How Is Cocoa Butter Extracted ?
To obtain pure and high-quality cocoa butter, cocoa beans from the Theobroma cacao tree undergo several specialized and precise processing steps. Each stage plays a critical role in preserving the flavor, aroma, and nutritional properties of this valuable fat.
Cocoa Bean
Cleaning
In the initial stage of cocoa processing, the beans must undergo thorough cleaning to remove impurities. Since the drying process often takes place directly on the ground, cocoa beans can contain unwanted materials such as sand, small stones, metal fragments, dried leaves, and other foreign particles.
These impurities must be completely eliminated before the beans proceed to subsequent stages to prevent equipment damage and ensure the quality and safety of the final cocoa butter.
Roasting
After fermentation and drying, cocoa beans undergo a roasting process. This critical step releases the unique flavors locked within the beans and triggers chemical reactions that develop the characteristic aroma and taste of cocoa.
The temperature and duration of roasting must be carefully controlled. Over-roasting can lead to undesirable bitterness, while under-roasting prevents the full development of flavor and aroma compounds essential for high-quality cocoa butter and chocolate production.
Sterilization
Cocoa bean sterilization is a process in which beans are subjected to controlled temperature and time conditions, either in batch or continuous mode, using dry heat, moist heat, or steam. The primary objective of this operation is to significantly reduce the microbial load and eliminate potentially pathogenic microorganisms that may have been introduced during harvesting, fermentation, drying, or transportation.
This process is typically carried out prior to roasting to control microbial populations before exposure to high roasting temperatures, although it can also be applied post-roasting. Proper sterilization conditions reduce the microbial load of cocoa beans to levels considered safe and acceptable according to industrial standards.
Crushing and Winnowing
After the roasting process, cocoa beans need to be separated from their hard outer shells. This step is performed through winnowing, where the outer husks are removed to isolate the inner part of the bean known as nibs.
Cocoa nibs contain both cocoa butter and cocoa solids, and they form the fundamental raw material for producing cocoa mass (cocoa liquor), which is the base for further cocoa butter extraction.
Cocoa Mass Grinding
Cocoa nibs are fed into grinders where cocoa butter is extracted and combined with cocoa solids, resulting in the production of cocoa mass—a thick, dark, and viscous paste. During this stage, cocoa butter and solids are integrated seamlessly, forming cocoa mass that serves as the base for chocolate production.
Various types of grinding machines are used to process the nibs, and the choice of equipment depends on factors such as:
Desired particle size
Amount of free fat (cocoa butter) released
Type of final chocolate product
This grinding process has a significant impact on the consistency, viscosity, and texture of the cocoa mass, which ultimately influences the quality of the finished chocolate.
Cocoa Butter Extraction
Cocoa mass is fed into a hydraulic press where it is subjected to high pressure (400 to 500 bar). This process effectively separates the cocoa butter (fat phase) from the cocoa cake (solid phase).
The extracted cocoa butter is a natural, pure fat that plays a vital role in determining the texture, flavor, and appearance of the final chocolate product. The remaining cocoa cake, in solid form, is typically ground to produce cocoa powder.
To further enhance its quality, the cocoa butter undergoes refining and deodorization processes. These steps help eliminate impurities and undesirable compounds, resulting in a higher purity, smoother flavor, and improved overall quality of the cocoa butter.
Cocoa butter
Cocoa Bean
Cleaning
In the initial stage of cocoa processing, the beans must undergo thorough cleaning to remove impurities. Since the drying process often takes place directly on the ground, cocoa beans can contain unwanted materials such as sand, small stones, metal fragments, dried leaves, and other foreign particles.
These impurities must be completely eliminated before the beans proceed to subsequent stages to prevent equipment damage and ensure the quality and safety of the final cocoa butter.
Roasting
After fermentation and drying, cocoa beans undergo a roasting process. This critical step releases the unique flavors locked within the beans and triggers chemical reactions that develop the characteristic aroma and taste of cocoa.
The temperature and duration of roasting must be carefully controlled. Over-roasting can lead to undesirable bitterness, while under-roasting prevents the full development of flavor and aroma compounds essential for high-quality cocoa butter and chocolate production.
Sterilization
Cocoa bean sterilization is a process in which beans are subjected to controlled temperature and time conditions, either in batch or continuous mode, using dry heat, moist heat, or steam. The primary objective of this operation is to significantly reduce the microbial load and eliminate potentially pathogenic microorganisms that may have been introduced during harvesting, fermentation, drying, or transportation.
This process is typically carried out prior to roasting to control microbial populations before exposure to high roasting temperatures, although it can also be applied post-roasting. Proper sterilization conditions reduce the microbial load of cocoa beans to levels considered safe and acceptable according to industrial standards.
Crushing and Winnowing
After the roasting process, cocoa beans need to be separated from their hard outer shells. This step is performed through winnowing, where the outer husks are removed to isolate the inner part of the bean known as nibs.
Cocoa nibs contain both cocoa butter and cocoa solids, and they form the fundamental raw material for producing cocoa mass (cocoa liquor), which is the base for further cocoa butter extraction.
Cocoa Mass Grinding
Cocoa nibs are fed into grinders where cocoa butter is extracted and combined with cocoa solids, resulting in the production of cocoa mass—a thick, dark, and viscous paste. During this stage, cocoa butter and solids are integrated seamlessly, forming cocoa mass that serves as the base for chocolate production.
Various types of grinding machines are used to process the nibs, and the choice of equipment depends on factors such as:
Desired particle size
Amount of free fat (cocoa butter) released
Type of final chocolate product
This grinding process has a significant impact on the consistency, viscosity, and texture of the cocoa mass, which ultimately influences the quality of the finished chocolate.
Cocoa Butter Extraction
Cocoa mass is fed into a hydraulic press where it is subjected to high pressure (400 to 500 bar). This process effectively separates the cocoa butter (fat phase) from the cocoa cake (solid phase).
The extracted cocoa butter is a natural, pure fat that plays a vital role in determining the texture, flavor, and appearance of the final chocolate product. The remaining cocoa cake, in solid form, is typically ground to produce cocoa powder.
To further enhance its quality, the cocoa butter undergoes refining and deodorization processes. These steps help eliminate impurities and undesirable compounds, resulting in a higher purity, smoother flavor, and improved overall quality of the cocoa butter.
Cocoa butter
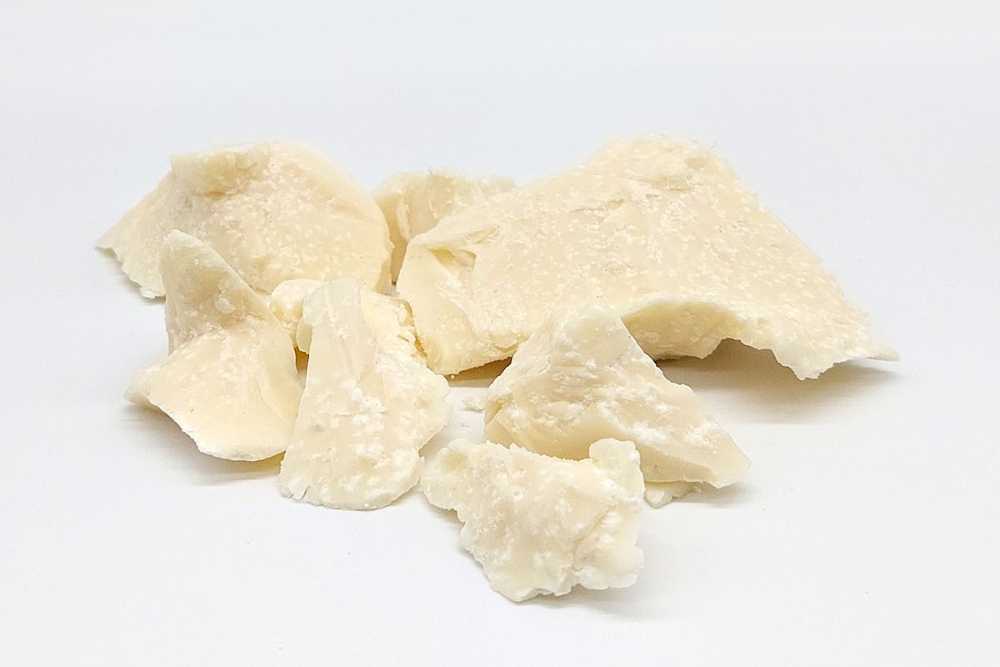
Natural vs. Deodorized Cocoa Butter : Which One to Choose ?
Cocoa butter is derived from the seeds of the Theobroma Cacao tree, rich in antioxidant polyphenols, methylxanthines like theobromine and caffeine, and essential minerals such as magnesium and potassium.
Natural (Non-Deodorized) Cocoa Butter
Natural cocoa butter retains its strong cocoa aroma and golden-yellow color. It is ideal for crafting premium chocolates and organic or natural cosmetic products where the cocoa scent is desirable.
Deodorized Cocoa Butter
Deodorized cocoa butter undergoes steam processing or filtration to remove its intense natural aroma and flavor, resulting in a lighter color and a neutral taste. This variant is widely used in:
Chocolates with added flavors or white chocolate
Fragrance-free cosmetic formulations
Pharmaceutical applications
Choosing between natural and deodorized cocoa butter depends on the desired flavor profile, product type, and functional properties required for the end application.

Applications of Cocoa Butter | From Food Industry to Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Cocoa butter plays a key role in various industries due to its soft texture, melting point that matches body temperature, and emollient and antioxidant properties:
Food Industry :
- Enhancing the production and quality of confectionery and chocolate products, particularly in texture and mouthfeel.
- Improving the thermal stability of chocolate products to withstand varying temperatures without developing fat bloom or whitening.
Cosmetic and Personal Care Industry :
- Moisturizing Creams and Lotions: Widely used for its emollient and hydrating properties, cocoa butter helps to nourish and soften the skin.
- Lip Balms: Acts as a natural protective barrier, preventing moisture loss and shielding lips from environmental stressors.
- Skincare and Anti-Aging Products: Utilized for its antioxidant-rich composition, cocoa butter aids in protecting the skin against oxidative stress, contributing to anti-wrinkle and rejuvenating formulations.
Pharmaceutical Industry :
- Suppository Production: Cocoa butter is widely used as a base for pharmaceutical suppositories due to its ability to melt at body temperature.
- Stable Base for Creams and Ointments: It serves as a reliable and stable carrier in medicinal creams and ointments.
- Oral Drug Formulations: Used to improve the texture and taste of oral medications, enhancing patient compliance.
Cocoa Butter Alternatives in the Chocolate and Confectionery Industry
Reducing production costs, enhancing thermal stability, and addressing the supply challenges of natural cocoa butter are the main reasons for using cocoa butter alternatives in chocolate and confectionery production.
What Are the Differences Between CBE, CBR, and CBS ?
- CBE (Cocoa Butter Equivalent):
CBE is a fat with a chemical structure similar to cocoa butter, extracted from sources like shea butter, illipe butter, and palm stearin. It can be blended directly with cocoa butter and is ideal for producing high-quality chocolates that retain similar melting behavior and flavor to natural cocoa butter. - CBR (Cocoa Butter Replacer):
CBRs have a different structure from cocoa butter and are typically made from partially hydrogenated oils. They are mainly used in confectionery coatings and compound chocolates, though in limited quantities, as they may affect the texture and flavor profile. - CBS (Cocoa Butter Substitute):
CBS fats are derived from coconut oil and palm kernel oil and are incompatible with cocoa butter. They have a lower melting point and are used in molded chocolates that do not require tempering. However, CBS carries the risk of fat bloom and changes in the chocolate’s appearance over time.
Choosing between CBE, CBR, or CBS depends on the product type, production process, desired flavor characteristics, and cost considerations.

Free download of the specialized book Cocoa Butter and Related Compounds
This reference book provides you with everything you need to know about the structure, properties, and uses of cocoa butter in chocolate making, cosmetic products and pharmaceuticals.
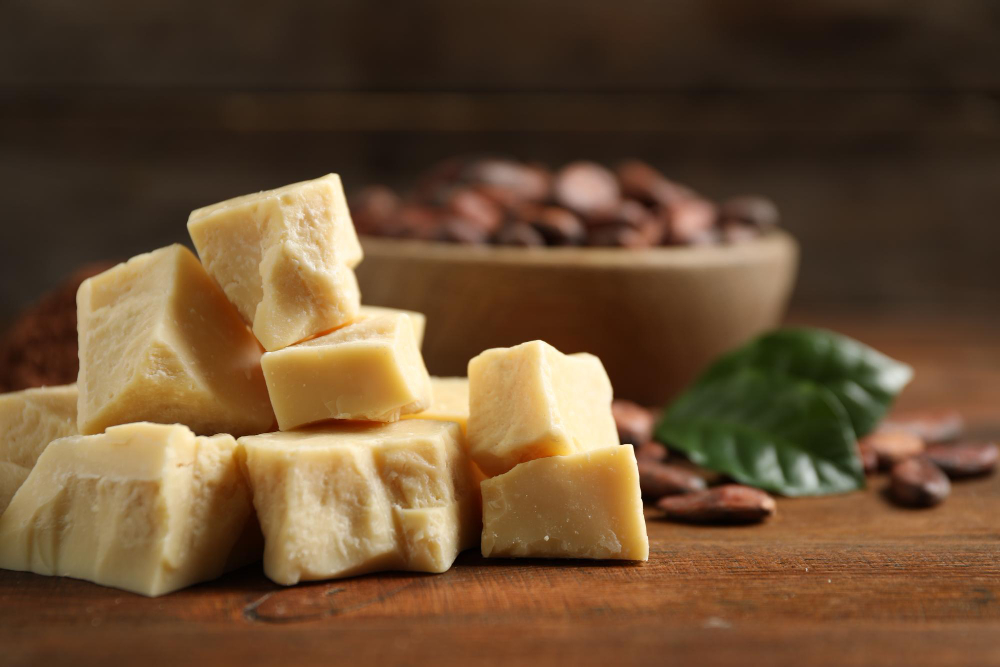

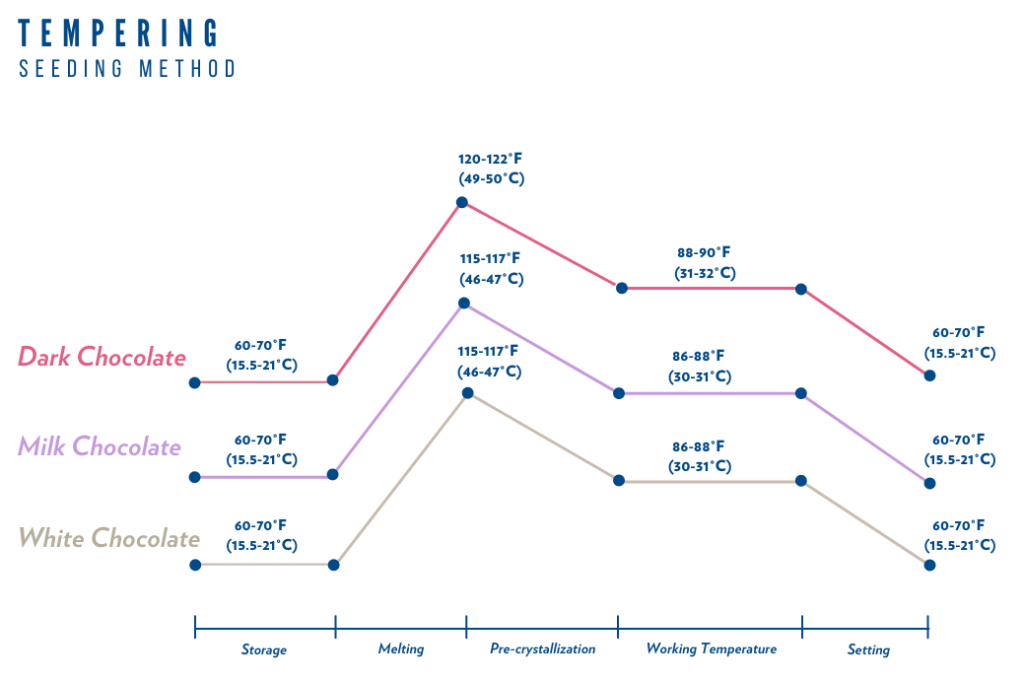
Chocolate Tempering Steps :
- Complete Melting: Heat the chocolate to 45–50°C to eliminate all existing fat crystals.
Cooling: Reduce the temperature to 26–28°C to initiate the formation of seed crystals, ensuring unstable forms are avoided through precise control.
Reheating: Raise the temperature to 30–32°C, allowing only the stable β5 crystal form to remain.
These temperature ranges may vary slightly depending on the type of chocolate—dark, milk, or white. Precise temperature control is essential for manufacturers and R&D teams to achieve chocolate with optimal quality, shelf life, and a professional appearance.
What Is Chocolate Tempering and Why Is It Crucial in Industrial Chocolate Production? | Complete Tempering Guide
Chocolate tempering is a controlled thermal process used to regulate the fat crystals in cocoa butter. Cocoa butter can crystallize in six different polymorphic forms, but only the stable β5 crystal form gives chocolate its glossy finish, desirable snap, and resistance to fat bloom (the whitish coating on chocolate surfaces).
Why Tempering Matters in Industrial Chocolate Production
Creates a smooth, shiny, and glossy appearance
Produces the desirable crisp texture and satisfying snap
Prevents fat bloom and maintains product quality over time
Ensures chocolate remains stable at room temperature and melts slowly
FAQ : Everything You Need to Know About Cocoa Butter
What Is the Best Storage Temperature for Cocoa Butter in Industrial Production and Warehousing ?
To maintain the quality of cocoa butter in industrial production and storage, it is recommended to store it at 18–20°C in an environment with relative humidity below 50%, away from direct light.
Under these conditions, cocoa butter is protected from fat bloom, oxidation, and crystal structure degradation, ensuring it remains in optimal condition for use in chocolate manufacturing, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Temperature and humidity control throughout the supply chain is critical for manufacturers and raw material warehouses to preserve the physical and chemical stability of cocoa butter.

Combining Cocoa Butter with Vegetable Fats in Formulations :
Enhancing Texture, Reducing Costs, and Increasing Product Stability
In industrial formulations, cocoa butter is often blended with vegetable fats such as shea butter, illipe butter, or palm stearin, commonly referred to as Cocoa Butter Equivalents (CBEs). This practice reduces production costs, enhances the thermal stability of chocolate, and adjusts the texture and melting point to meet market demands.
For manufacturers, this approach allows for the customization of physical and sensory properties in chocolates and cosmetic products, while also helping to manage supply challenges and the price volatility of natural cocoa butter.
Summary : Cocoa Butter in Chocolate Production ; From Fatty Acid Composition to Industrial Alternatives and Production Optimization
Cocoa butter is a key and strategic ingredient in the chocolate industry. Its fatty acid composition, bean origin, and production processes directly impact the flavor, texture, and overall quality of the final product. A scientific understanding of these factors, combined with precise control over processes like crystallization and tempering, enables R&D teams and manufacturers to optimize product quality and shelf stability.
Moreover, when the cost and supply of natural cocoa butter become challenging, the smart use of alternatives like CBE (Cocoa Butter Equivalents), CBR (Cocoa Butter Replacers), and CBS (Cocoa Butter Substitutes) offers opportunities for cost reduction, improved thermal stability, and enhanced profitability.








