Why Does the Type of Alkalizing Agent Matter in Cocoa Powder Formulation ?
The type of alkalizing agent used in cocoa powder affects much more than just color—it plays a critical role in the flavor profile, functional behavior, and stability of cocoa in dairy systems like chocolate milk, UHT beverages, and refrigerated products.
Selecting the right alkalizing base (e.g., NaOH, KOH, or K₂CO₃) significantly influences:
Color intensity and tone
Flavor sharpness or smoothness
Viscosity and mouthfeel
Oxidative stability during shelf life
The alkalizing agent also affects chemical indicators like pH, buffer capacity, and interactions with dairy proteins and minerals. key factors for maintaining sensory and visual consistency in chocolate milk.
What Is Alkalization (Dutch Process ) in Cocoa and Why Is It Important in Chocolate Milk?
The Dutch Process is a cocoa alkalization technique in which cocoa nibs are treated with alkaline salts to modify their physical and chemical properties. This process not only mellows the flavor and reduces acidity, but also intensifies the color and enhances cocoa’s functionality in dairy systems.
In dairy applications, these changes directly impact:
Color uniformity
Flavor depth and balance
Dispersibility and texture in the final beverage
Choosing the right type of alkalizing agent isn’t just about shade. it’s a formulation decision that shapes the final product’s performance.
Final Product pH and Microbial Stability
pH is a key factor in controlling microbial growth and improving the shelf life of chocolate milk :
NaOH rapidly raises the pH, but may promote spoilage during long-term storage.
K₂CO₃ provides more stable pH, enhancing color retention and long-term functional consistency.
KOH offers both a significant pH shift and better pH uniformity in dairy systems.
Viscosity and Mouthfeel in Final Application
Cocoa’s effect on viscosity and sensory perception is crucial in flavored dairy :
KOH increases body and creaminess, ideal for “full-bodied” products.
NaOH results in lighter viscosity and reduced sensory density.
K₂CO₃ delivers a well-balanced texture, preferred in kid-friendly or mild products.
Color Stability and Visual Uniformity Over Shelf Life
Color is a major cue in consumer perception and product appeal :
NaOH yields darker brown tones but may fade over time.
KOH provides a rich, stable hue ideal for premium applications.
K₂CO₃ imparts reddish-brown tones, often favored in pediatric or niche products.
Flavor Perception and Sensory Attributes
The type of alkalizing agent influences bitterness, smoothness, and overall flavor profile :
NaOH may result in increased bitterness.
KOH imparts a stronger aroma and more pronounced cocoa taste.
K₂CO₃ delivers a mild, balanced taste commonly preferred in dairy applications.
Total Polyphenol Content (TPC) and Antioxidant Capacity
Cocoa is a natural source of polyphenols; however, alkalization can reduce TPC levels :
NaOH tends to reduce TPC more significantly.
KOH maintains a better balance between alkalization and TPC preservation.
K₂CO₃ provides superior antioxidant retention and is often favored for nutritionally fortified dairy products.
Thermal Stability and Compatibility with Heat Processes
(UHT / Pasteurization)
UHT dairy products require cocoa powders with thermal stability :
K₂CO₃ leads to more stable pH after heating.
NaOH offers less pH stability under heat stress.
This makes K₂CO₃ an ideal option for export-oriented products or extended shelf-life dairy.
As previously discussed, the impact of alkalizing agents on cocoa powder goes far beyond color. The alkalization process alters essential physicochemical attributes that directly affect cocoa’s performance in dairy applications like chocolate milk. Below are the most important parameters influenced:
Key Chemical Parameters Influenced by Alkalization
Balancing flavor, texture, pH, color, TPC, and thermal performance is key to selecting the right alkalized cocoa powder especially for specific dairy applications like UHT, pasteurized milk, or fortified exports.
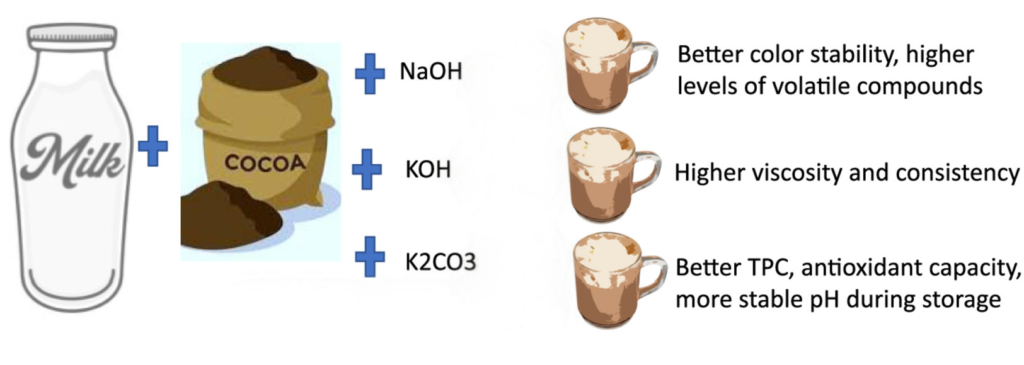

Which Alkalizing Agent Is Best for Chocolate Milk? A Comparison of NaOH, KOH, and K₂CO₃
The type of alkalizing agent used during cocoa processing has a direct impact on key functional properties in dairy applications. Each agent affects color, pH, viscosity, flavor retention, and sensory performance differently, making the choice highly product-specific.
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) increases color intensity and enhances volatile compound release, but may also increase bitterness and reduce flavor balance in chocolate milk.
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) improves cocoa richness and creaminess, with a smoother mouthfeel and fuller sensory profile—ideal for high-protein or indulgent dairy drinks.
Potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) provides excellent pH stability and antioxidant retention. It enhances nutritional positioning and is well-suited for UHT and export-oriented dairy products with extended shelf life.
Which alkalizing agent performs best in high-protein dairy applications?
KOH increases viscosity and enhances creaminess, making it ideal for high-protein milk formulations. It also provides greater flavor retention and better compatibility with functional ingredients like fiber and minerals.
Can alkalizing agents be used in combination during cocoa processing?
Yes, multiple agents (e.g., NaOH + K₂CO₃) can be combined to balance performance traits. However, blending must be carefully controlled to avoid unwanted shifts in pH or off-flavors in industrial settings.
Do alkalizing agents affect flavor stability during shelf life?
Absolutely. Agents like NaOH tend to increase bitterness and reduce flavor stability. In contrast, K₂CO₃ preserves smoother cocoa notes and supports longer-lasting sensory balance over time.

Alkalizing agent is just one of the key variables in cocoa formulation! To design a formulation that delivers unmatched quality, stability, and flavor, read the full article now :
5 important factors for selection cocoa powder for dairy
- Related articles
Conclusion : Every Dairy Product Needs Its Own Specialized Alkalized Cocoa Powder
In dairy formulations, the impact of the alkalizing agent on cocoa powder extends far beyond color. It directly influences the final product’s texture, flavor, viscosity, and shelf-life stability, making it a decisive factor in formulation performance.












