Why is Cocoa Powder Solubility Critical in Chocolate Milk and Dairy Beverages?
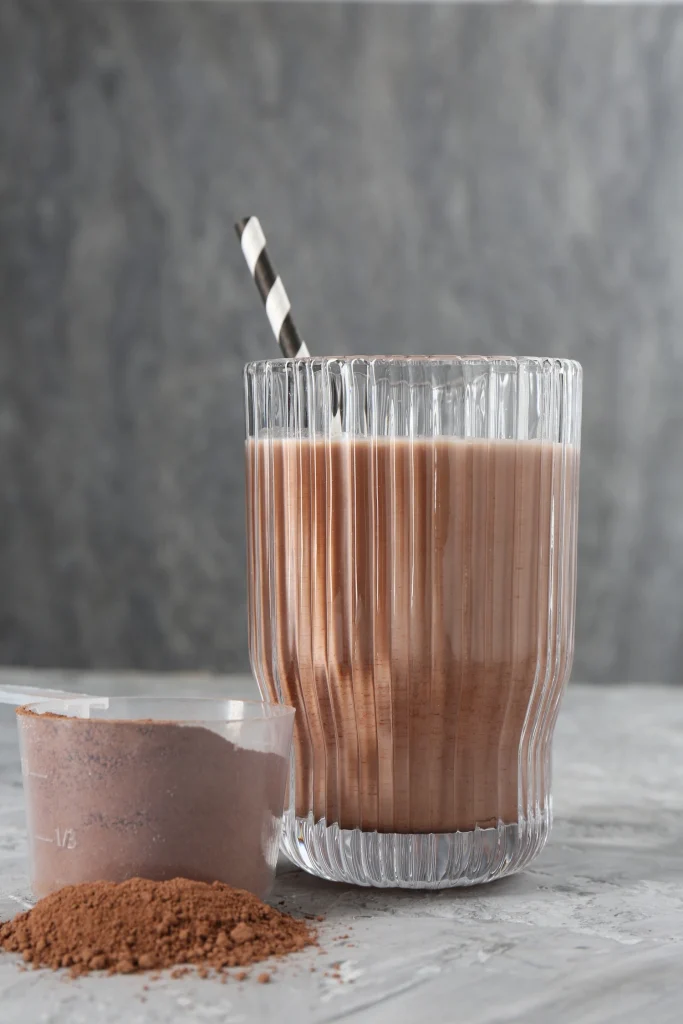
In dairy beverage production, especially chocolate milk, the dispersibility of cocoa powder is a key factor for formulation success. Poor solubility or sedimentation isn’t just a visual flaw — it directly affects product stability, texture uniformity, consumer experience, and shelf durability.
In today’s competitive market, products that separate or curdle a few days after production lose appeal. A formulation lacking in stability control risks damaging the brand’s reputation and losing market share over time.
The Hidden Costs of Cocoa Powder Sedimentation in Dairy: From Lost Sales to Declining Product Quality
Cocoa powder sedimentation isn’t just a technical issue ; it leads to hidden long-term costs for brands and manufacturers:
Increased Formulation Costs:
To counter sedimentation, higher amounts of stabilizers and emulsifiers are required, which not only raises production costs but can also cause product defects like curdling or syneresis.Quality Control Risks:
Products with visible sedimentation are more likely to fail quality assessments, resulting in costly batch reworks or rejections.Brand Reputation Damage:
Inconsistent product appearance or texture signals poor quality control, potentially harming brand credibility in the long run.
Choosing a cocoa powder with excellent suspension stability and dispersibility is a critical factor in the formulation strategies of leading dairy producers.
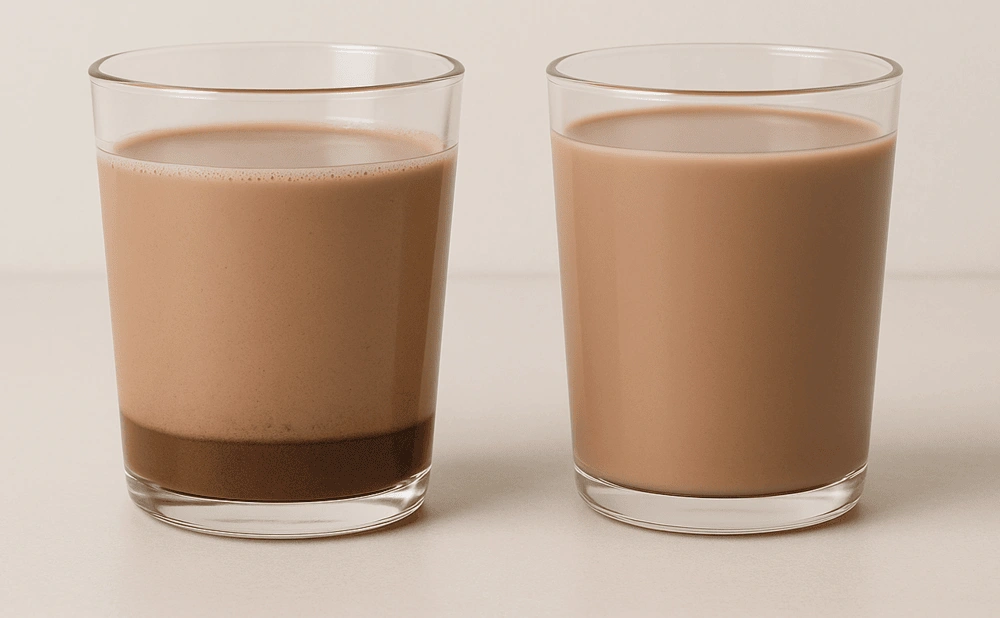
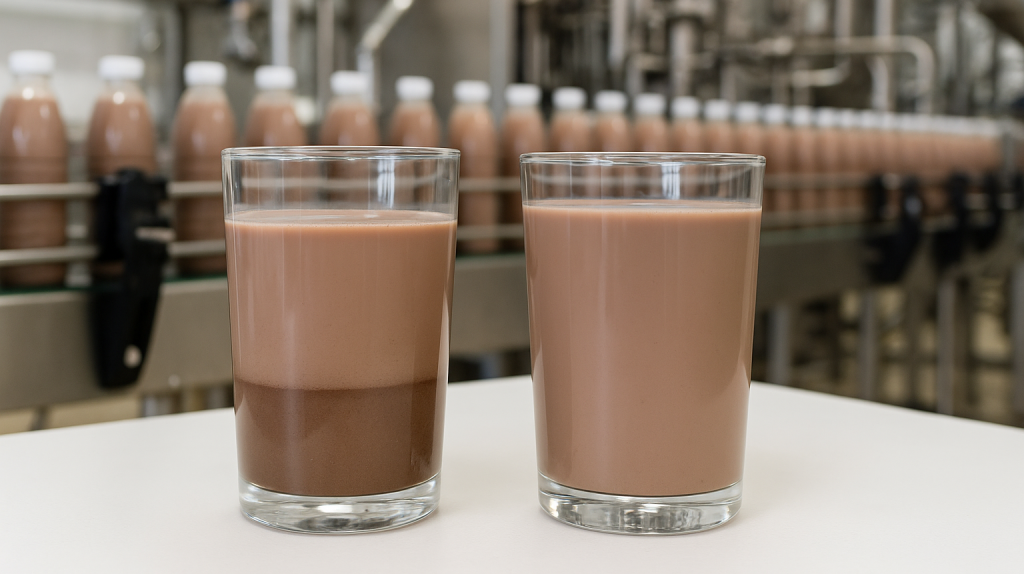
Visual Impact of Cocoa Sedimentation on Dairy Products
Even with instructions like “shake well before use,” a product that stays visually uniform stands out on the shelf — signaling quality and reliability from the first glance.
Sedimentation leads to phase separation:
A lighter layer on top
A darker, denser layer at the bottom
Consumers often perceive this as a sign of poor quality or expired stock, even if safety is uncompromised.
Additionally, in production lines, uncontrolled sedimentation causes inconsistency between bottles ; especially problematic in high-speed filling processes. Professional brands prevent this by using cocoa with high dispersibility, optimized particle size distribution, and additives like lecithin or CMC, ensuring product uniformity across the shelf life.
How Does Cocoa Sedimentation Affect the Taste and Texture of Chocolate Milk ?
Sedimentation isn’t just a cosmetic flaw; it disrupts the consumer experience. As cocoa particles settle, the drink’s flavor becomes inconsistent ; watery at first, with an overly intense, bitter taste at the bottom.
Moreover, sedimentation affects viscosity, causing uneven textures ; some parts of the drink may feel thin while others are thick and unpleasant. This inconsistency is unacceptable, especially in premium dairy beverages.
Using cocoa powder with controlled particle size, balanced fat content, and proper alkalization helps stabilize flavor and texture throughout the product’s shelf life.
Cocoa Powder Sedimentation in Dairy: A Challenge Impacting Appearance, Taste, and Texture
Sedimentation of cocoa powder in dairy products, particularly in chocolate milk, is a major formulation challenge. Beyond visual defects, it alters taste and texture, reducing sensory quality and customer satisfaction ; ultimately leading to declining sales if not properly managed.


How Does Cocoa Particle Size Affect Stability and Sedimentation in Dairy ?
Particle size is a critical factor in the sedimentation rate and suspension stability of cocoa in dairy beverages. Research indicates:
Optimal particle size: 24 to 28 microns provides maximum stability.
Smaller particles: They settle slower, but if too fine, they increase viscosity and may create an undesirable mouthfeel.
Uniform particle distribution: Achieved through processes like micronization, ensuring better suspension and product consistency.
Accurate measurement and control of particle size are essential in formulation to prevent sedimentation and maintain uniform quality.
How Does Alkalization and Type of Alkali Impact Cocoa Solubility and Stability in Dairy ?
Alkalization modifies the chemical structure of cocoa particles, enhancing their dispersibility in dairy systems. During this process:
Cocoa’s pH increases, making particles more hydrophilic.
Alkalis like K₂CO₃ (potassium carbonate) or NaOH (sodium hydroxide) are used.
This enhances wettability and improves interactions with milk proteins, leading to more stable networks. However, excessive alkalization may reduce polyphenol content and diminish cocoa’s antioxidant properties.

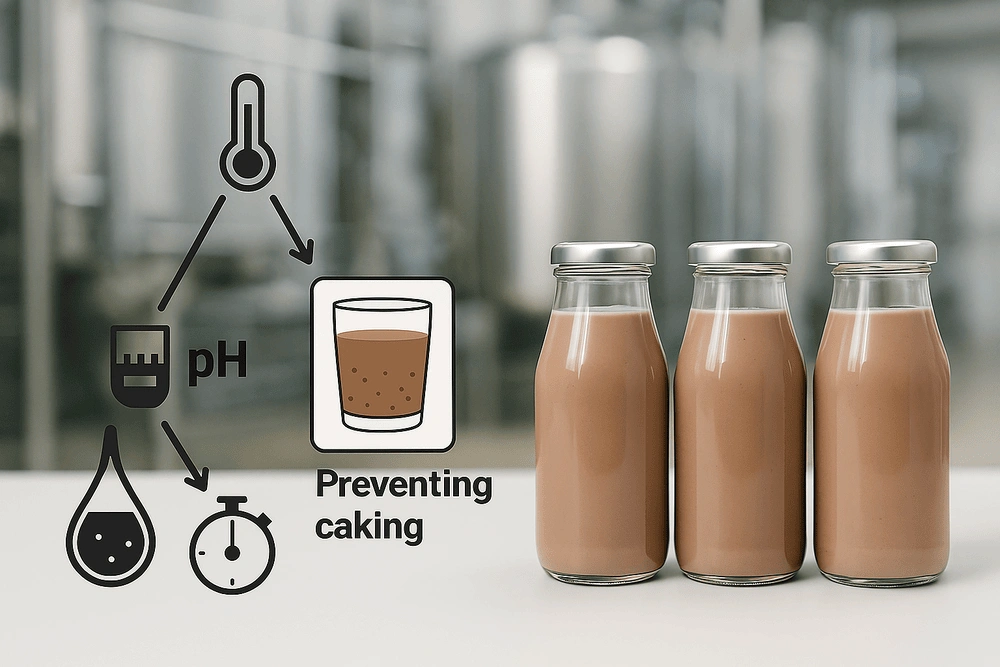
What Are the Best Temperature, pH, and Time Conditions to Prevent Cocoa Sedimentation in Dairy ?
Studies suggest that optimal conditions for physical stability in cocoa-dairy systems are:
pH: ~6.6
Homogenization temperature: 75°C
UHT process: 135°C for 10 seconds
At pH 6.6, protein absorption onto cocoa particles is maximized, forming stable networks. Overheating (e.g., 118°C for over 20 minutes) risks flocculation and increased sedimentation.
Additionally, using specialized stabilizers like carrageenan and CMC, alongside precise control of temperature and pH, helps preserve product uniformity and desirable texture.
Why Does Cocoa Powder Sediment in Dairy ? Causes and Solutions
How Do Cocoa Particle Size and Fat Content Affect Dispersibility ?
Particle size and fat content are two critical factors influencing the dispersibility and suspension stability of cocoa powder in dairy beverages like chocolate milk.
According to research published in the Physical Stability of Chocolate Milk, particles measuring 6.3 to 7.9 microns (after heating at 118°C) effectively form protein-cocoa networks that delay sedimentation. Finer particles increase surface contact with the liquid, enhancing wettability and overall dispersibility. However, if the particles are too fine, the beverage can become overly thin, altering the mouthfeel.
📌 To maximize suspension stability and minimize sedimentation, a balance between particle size and fat content is essential:
Particle size: 24–28 microns (or slightly less) is recommended for better suspension.
Fat content: Reducing cocoa fat to 10-12% improves wettability and decreases reliance on emulsifiers.

Choosing the right cocoa powder defines the line between ordinary and premium.
Discover 5 key factors to create a formulation unmatched in quality, stability and taste.
- Related articles
Why Does Cocoa’s Molecular Structure Hinder Complete Dissolution in Milk ?
Cocoa powder’s difficulty in dissolving in water and dairy stems from its inherent molecular structure and composition. Non-polar fats and hydrophobic cell walls make cocoa particles repel water rather than absorb it, causing them to float instead of dispersing evenly. Additionally, polyphenols bound within the cell matrix further enhance hydrophobicity, reducing the dispersibility of cocoa in aqueous phases.
Without emulsifiers or treatments like alkalization – which increases pH and enhances hydrophilicity – cocoa powder remains unstable in milk and quickly sediments.
How Do Cocoa Fat, Polyphenols and Fiber Affect Solubility in Milk and Dairy ?
The fat, polyphenols, and fibers in cocoa significantly influence the physical stability of dairy beverages:
Fat: Creates a surface coating on particles, promoting aggregation and phase separation over time.
Polyphenols and fibers: Interact with milk proteins and colloidal components, diminishing suspension stability and contributing to sediment formation.
To mitigate these effects, formulators use stabilizers such as carrageenan and carefully adjust fat levels to improve uniformity, prevent sedimentation, and enhance texture and appearance.
The Role of Cocoa Powder’s Chemical Structure and Physical Properties in Solubility and Stability in Dairy Products
In the dairy industry, one of the common technical challenges is controlling sedimentation and enhancing suspension stability in chocolate milk and cocoa-based beverages. The complex molecular structure of cocoa — along with its fat, polyphenols, and dietary fiber — influences how particles behave in aqueous and dairy environments. Here’s why cocoa resists dissolving in milk, which compounds intensify sedimentation, and how alkalized versus natural cocoa impacts dispersibility and shelf stability.

Alkalized vs. Natural Cocoa: Which Dissolves Better in Milk?
Alkalized cocoa, produced via alkalization, possesses structural properties that improve solubility and suspension stability in dairy compared to natural cocoa. The process raises the cocoa’s pH, increasing particle hydrophilicity, reducing water repellency, and enhancing wettability.
Research from Physical Stability of Chocolate Milk (2022) shows that alkalized cocoa forms modified surfaces that resist aggregation and sedimentation. It interacts more effectively with milk proteins to create a stable network that withstands gravity and prevents phase separation.
These attributes make alkalized cocoa the preferred choice in the dairy industry for ready-to-drink chocolate milk — minimizing sedimentation, maintaining texture uniformity, and extending shelf life while reducing formulation costs and enhancing sensory quality.

How Does Spray Drying Technology Improve Cocoa Powder Solubility ?
Spray drying technology converts cocoa into powders with a porous and uniform structure through a controlled drying process. This structure:
Enables faster solubility in water or milk.
Is ideal for producing instant cocoa powders, widely used in the dairy industry.
These technologies, combined with the use of appropriate emulsifiers and stabilizers, contribute to the production of homogeneous dairy beverages with better appearance, texture, and taste.
Modern Technologies to Improve Dispersibility and Stability of Cocoa Powder in Dairy Industries
One of the common challenges in producing dairy beverages like chocolate milk is the instability of cocoa suspensions, which often leads to cocoa particle sedimentation. To address this issue, advanced processing technologies for cocoa powder have been developed, aiming to improve solubility, reduce hydrophobicity of cocoa particles, and enhance suspension stability.

Which Hydrocolloids Help Stabilize Cocoa in Milk ?
Which Hydrocolloids Help Stabilize Cocoa in Milk?
Hydrocolloids or natural gums play a key role in increasing viscosity and stabilizing suspended cocoa particles in dairy beverages. The most effective hydrocolloids include:
CMC (Carboxymethyl Cellulose):
Increases viscosity, slows particle movement, and prevents sedimentation.Carrageenan:
At low concentrations, forms gel-like networks that keep cocoa particles suspended in the liquid.
Combining these hydrocolloids, often alongside emulsifiers, creates a multi-layered stabilization system that enhances product appearance, flavor consistency, and mouthfeel.
Which Additives and Stabilizers Prevent Cocoa Powder Sedimentation in Dairy ?
In dairy manufacturing, sedimentation of cocoa particles and phase separation are common challenges, especially in chocolate milk and cocoa-based drinks. To address this, the use of emulsifiers, stabilizers and specialized hydrocolloids is essential for ensuring physical stability, maintaining a uniform texture and preserving flavor throughout the product’s shelf life.
How Do Lecithin and Emulsifiers Prevent Cocoa Sedimentation in Dairy ?
Lecithin and other emulsifiers work by reducing the surface tension between water and fat, improving the wetting of cocoa particles and coating their surfaces. This action prevents particles from sticking together and forming sediment, ensuring a stable suspension in dairy beverages and contributing to a smoother, more consistent drink.

What Is the Difference Between Instant Cocoa Powder and Regular Cocoa Powder ?
Regular cocoa powder contains more natural fat and has a hydrophobic surface, making it difficult to dissolve in liquids. It tends to clump and settle, especially in cold drinks, resulting in an uneven texture.
In contrast, Instant Cocoa Powder is produced through an agglomeration process, where cocoa particles bind together to form larger, porous granules that:
Dissolve faster and more easily in both hot and cold liquids.
Are less prone to clumping.
Create a smoother texture and more balanced flavor in beverages.
Enhance solubility in industrial production lines, reducing preparation time and improving process efficiency.
Summary : The Best Non-Sediment Cocoa Powder for the Dairy Industry
Choosing a non-sediment cocoa powder for dairy applications goes beyond flavor and color. Key factors such as solubility, particle size, fat content, processing method, and stabilizing additives critically influence the final product’s stability. To develop a formulation free of sedimentation, phase separation, or flavor degradation, careful selection of cocoa powder and its complementary processes is essential.
For a comprehensive guide, refer to the article “5 important factors for selection cocoa powder for dairy ”












